

Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
Subsections
The purpose of this lab is to use Maple to study solids of revolution.
Solids of revolution are created by rotating curves in the x-y plane
about an axis, generating a three dimensional object. The specific properties of them that we wish to study are their graph and volume.
So far we have used the integral mainly to to compute areas of plane regions.
It turns out that the definite integral can also be used to calculate
the volumes of certain types of three-dimensional solids. The class of
solids we will consider in this lab are called Solids of
Revolution because they can be obtained by revolving a plane region
about an axis.
As a simple example, consider the graph of the function 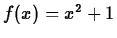 for
for
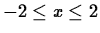 which you can plot on Maple:
which you can plot on Maple:
> f := x-> x^2+1;
> plot(f(x),x=-2..2);
If we take the region between the graph and the x-axis and revolve it
about the x-axis, we obtain a 3-D solid.
To plot this solid of revolution using Maple, the revolve command can be used. All of the procedures described in this lab are part of the CalcP7 package, which must be loaded first. The syntax for revolve when revolving  about the
about the 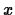 -axis over the interval
-axis over the interval
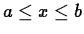 is:
is:
> revolve(f(x),x=a..b);
If you revolve the area under the graph of 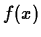 for
for
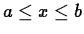 about the
about the 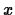 -axis, the volume is given by
-axis, the volume is given by
The integral formula given above for the volume of a solid of
revolution comes, as usual, from a limit process. Recall the
rectangular approximations we used for plane regions. If you think of
taking one of the rectangles and revolving it about the x-axis, you
get a disk whose radius is the height 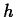 of the rectangle and
thickness is
of the rectangle and
thickness is 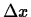 , the width of the rectangle. The volume of
this disk is
, the width of the rectangle. The volume of
this disk is
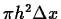 . If you revolve all of the rectangles in
the rectangular approximation about the x-axis, you get a solid made
up of disks that approximates the volume of the solid of revolution
obtained by revolving the plane region about the x-axis.
. If you revolve all of the rectangles in
the rectangular approximation about the x-axis, you get a solid made
up of disks that approximates the volume of the solid of revolution
obtained by revolving the plane region about the x-axis.
To help you visualize this approximation of the volume by disks, the
LeftDisk procedure has been written. The syntax for this command is similar to that for revolve, except that the number of
subintervals must be specified. The examples below produce
approximations with five and ten disks. The last example produces the exact solid of revolution.
> with(CalcP7):
> f := x -> x^2+1;
> LeftDisk(f(x),x=-2..2,5);
> LeftDisk(f(x),x=-2..2,10);
> revolve(f(x),x=-2..2);
The revolve command has optional arguments. A third argument can be added to specify a different axis of revolution. For instance, we may want to revolve the graph of 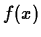 about the line
about the line 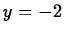 instead of the default
instead of the default 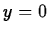 . Also, the nocap argument can speed up the plotting process by only plotting the surface generated by revolving the curve instead of solid generated by revolving the area. Below is an example of what the 3-D solid looks like when revolving
. Also, the nocap argument can speed up the plotting process by only plotting the surface generated by revolving the curve instead of solid generated by revolving the area. Below is an example of what the 3-D solid looks like when revolving 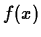 about the line
about the line 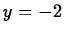 .
.
> revolve(f(x),x=-2..2,y=-2,nocap);
You can also plot a solid of revolution formed by revolving the area between two functions. Try the following
examples.
> plot({5,x^2+1},x=-2..2);
> revolve({5,x^2+1},x=-2..2);
As stated earlier, the volume of the solid obtained by revolving the region under the graph of 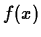 , above the
, above the 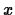 -axis, over the interval
-axis, over the interval
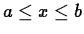 is given by
is given by
Therefore, the volume of the solid obtained by revolving the region between the graph of 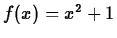 and the
and the 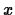 -axis about the
-axis about the 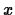 -axis can be determined from the integral
-axis can be determined from the integral
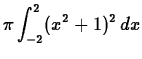 .
.
In order to calculate the volume of a solid of revolution, you can either use the int command implementing the formula above or use the Maple procedure RevInt which sets up the integral for you. The Maple commands evalf
and value can be used to obtain a numerical or analytical value. Approximations to the volume of the solid of revolution can be found using the LeftInt. Try the examples below to see the different types of output.
> Pi*int(f(x)^2,x=-2..2);
> evalf(Pi*int(f(x)^2,x=-2..2));
> RevInt(f(x),x=-2..2);
> value(RevInt(f(x),x=-2..2));
> evalf(RevInt(f(x),x=-2..2));
> evalf(LeftInt(f(x),x=-2..2,50));
- For the function
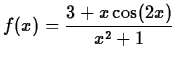 over the interval
over the interval
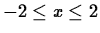 ,
,
- Plot
 over the given interval.
over the given interval.
- Plot the approximation of the solid of revolution using
 with 12 disks.
with 12 disks.
- Plot the solid formed by revolving
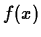 about the
about the 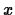 -axis.
-axis.
- Plot the solid formed by revolving
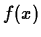 about the line
about the line 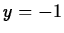 .
.
- Find the exact volume of the solid of revolution about the
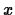 -axis using the integral formula.
-axis using the integral formula.
- Find the exact volume of the solid of revolution using the RevInt command and label your output exact.
- Find the minimum number of subintervals needed to approximate the volume of the solid of revolution about the
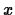 -axis using LeftInt with error no greater than 0.01.
-axis using LeftInt with error no greater than 0.01.
- What function's graph can be revolved about the
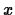 -axis to obtain a sphere of radius
-axis to obtain a sphere of radius 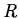 ? Use this function and the RevInt command to prove that the volume of a sphere is
? Use this function and the RevInt command to prove that the volume of a sphere is
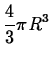 .
.
- Six years ago, Kevin Nordberg and James Rush (both
class of '98) were asked to design a drinking glass by revolving a
suitable function about the
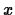 axis. Here is the function they came
up with.
axis. Here is the function they came
up with.
They obtained the shape of their glass by revolving this function
about the 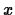 axis over the interval
axis over the interval ![$[-1,2]$](img20.png) . The Maple command
they used to define this function is given below.
. The Maple command
they used to define this function is given below.
> f := x -> piecewise(x<-3/4,-2*x-1/2,x<0,1/6,x^(2/3)+1/6);
Plot this function (without revolving it) over the interval
![$[-1,2]$](img20.png) and identify the formula for each part of the
graph. Then, revolve this function about the
and identify the formula for each part of the
graph. Then, revolve this function about the 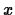 axis over the
same interval and comment on the glass Kevin and Jim
designed. Finally, compute the volume of the part of this glass that
could be filled with liquid, assuming the stem is solid. (Hint - your
integral will involve only one of the formulas used to define the
function.)
axis over the
same interval and comment on the glass Kevin and Jim
designed. Finally, compute the volume of the part of this glass that
could be filled with liquid, assuming the stem is solid. (Hint - your
integral will involve only one of the formulas used to define the
function.)


Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
Dina Solitro
2001-11-27
![]() about the
about the ![]() -axis over the interval
-axis over the interval
![]() is:
is:
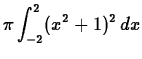 .
.
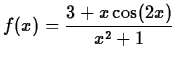 over the interval
over the interval
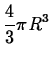 .
.
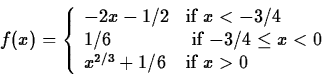
![]() and identify the formula for each part of the
graph. Then, revolve this function about the
and identify the formula for each part of the
graph. Then, revolve this function about the ![]() axis over the
same interval and comment on the glass Kevin and Jim
designed. Finally, compute the volume of the part of this glass that
could be filled with liquid, assuming the stem is solid. (Hint - your
integral will involve only one of the formulas used to define the
function.)
axis over the
same interval and comment on the glass Kevin and Jim
designed. Finally, compute the volume of the part of this glass that
could be filled with liquid, assuming the stem is solid. (Hint - your
integral will involve only one of the formulas used to define the
function.)