

Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
Subsections
The purpose of this lab is to use Maple to study applications of
exponential and logarithmic functions. These are used to model many
types of growth and decay, for example bacterial growth and
radiaoctive decay. This lab also describes applications of exponential
and logarithmic functions for heating and cooling and to medicine dosage
The simple model for growth is
exponential growth, where
it is assumed that
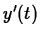 is proportional to
is proportional to 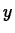 . That is,
. That is,
Separating the variables and integrating (see section 4.4 of the text),
we have
so that
In the case of exponential growth, we can drop the absolute value
signs around 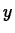 , because
, because 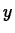 will always be a positive quantity.
Solving for
will always be a positive quantity.
Solving for 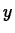 , we obtain
, we obtain
which we may write in the form 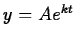 , where
, where 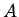 is an
arbitrary positive constant.
is an
arbitrary positive constant.
In a sample of a radioactive material, the
rate at which atoms decay is proportional to the amount of material present.
That is,
where 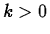 is a constant. This is the same equation as in exponential growth,
except that
is a constant. This is the same equation as in exponential growth,
except that 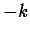 replaces
replaces 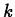 . The solution is
. The solution is
where 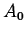 is a positive constant. Physically,
is a positive constant. Physically, 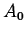 is the amount of
material present at
is the amount of
material present at 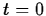 .
.
Radioactivity is often expressed in terms of an element's half-life.
For example, the half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. This statement means
that for any given sample of
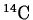 , after 5730 years, half of it
will have undergone decay.
So, if the half-life is of an element Z is
, after 5730 years, half of it
will have undergone decay.
So, if the half-life is of an element Z is 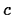 years, it must be
that
years, it must be
that
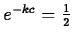 , so that
, so that 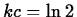 and
and
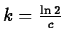 .
.
What is usually called Newton's law of cooling is a simple model for
the change in temperature of an object that is in contact with an
environment at a different temperature. It says that the rate of
change of the temperature of an object is proportional to the
difference between the object's temperature and the temperature of the
environment. Mathematically, this can be expressed as the differential
equation
where 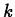 is the constant of proportionality and
is the constant of proportionality and
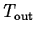 is
the temperature of the environment. Using a technique called
separation of variables it isn't hard to derive the solution
is
the temperature of the environment. Using a technique called
separation of variables it isn't hard to derive the solution
where 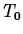 is the temperature of the object at
is the temperature of the object at 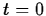 .
.
If a drug is administered to a patient intravenously, the concentration
jumps to its highest level almost immediately. The concentration
subsequently decays exponentially. If we use 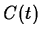 to represent the concentration at time t, and
to represent the concentration at time t, and 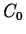 to represent the
concentration just after the dose is administered then our exponential
decay model would be given by
to represent the
concentration just after the dose is administered then our exponential
decay model would be given by
A problem facing physicians is the fact that for most drugs, there is
a concentration, 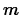 , below which the drug is ineffective and a
concentration,
, below which the drug is ineffective and a
concentration, 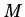 , above which the drug is dangerous. Thus the
physician would like the have the concentration
, above which the drug is dangerous. Thus the
physician would like the have the concentration 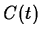 satisfy
satisfy
This means that the initial dose must not produce a concentration
larger than 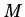 and that another dose will have to be administered
before the concentration reaches
and that another dose will have to be administered
before the concentration reaches 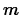 .
.
The main functions you need are the natural exponential and
natural logarithm. The Maple commands for these functions are
exp and ln. Here are a few examples.
> f := x -> exp(-2*x);
> simplify(ln(3)+ln(9));
> ln(exp(x));
> simplify(ln(exp(x)),assume=real);
The assume=real is needed in the command above, because Maple
usually works with complex variables. The command for base 10
logarithms is log10. Here are some examples. Note how Maple
likes to convert base 10 logarithms to natural logarithms.
> log10(100);
> simplify(log10(100));
> simplify(log10(a)-log10(b),assume=real);
Sometimes you need to use experimental data to determine the value of
constants in models. For example, suppose that for a particular drug,
the following data
were obtained. Just after the drug is injected, the concentration is
1.5 mg/ml (milligrams per milliliter). After four hours the
concentration has dropped to 0.25 mg/ml. From this data we can
determine values of 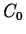 and
and 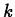 as follows. The value of
as follows. The value of 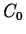 is the
initial concentration, so we have
is the
initial concentration, so we have
To find the value of 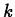 we need to solve the equation
we need to solve the equation
which we get by plugging in 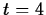 and using the data
and using the data
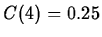 . Maple commands for solving for
. Maple commands for solving for 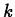 and defining and
plotting the function
and defining and
plotting the function 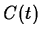 are shown below.
are shown below.
> k1 := solve(0.25=1.5*exp(-4*k),k);
> C1 := t -> 1.5*exp(-k1*t);
> plot(C1(t),t=0..6);
- An example of common logarithms is the decibel scale, particularly used for measuring loudness. (The decibel unit is named in honor of Alexander G. Bell (1847-1922), inventor of the telephone.) If
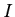 is the intensity of sound in watts per square meter, the decibel level of the sound is
is the intensity of sound in watts per square meter, the decibel level of the sound is
where 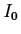 is an intensity corresponding roughly to the faintest sound that can be heard.
is an intensity corresponding roughly to the faintest sound that can be heard.
When tuning the rock band's equipment before the concert in a big concert hall, an audio engineer finds that in order to maintain appropriate loudness in this hall, he needs to increase the power of the amplifiers in comparison with the level used for the previous concert in a hall of smaller size.
- What does the doubling the intensity add to the level of loudness in decibels?
- By what factor
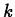 will the engineer have to multiply the intensity of the sound to add 20 to the sound level for the next concert of the band on the stadium?
will the engineer have to multiply the intensity of the sound to add 20 to the sound level for the next concert of the band on the stadium?
- The cry of a blue whale can be heard nearly 500 miles away, reaching an intensity of (6.3 x
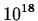 )
)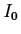 . Using the same formula for loudness given in exercise 1, determine the decibel level of this sound.
. Using the same formula for loudness given in exercise 1, determine the decibel level of this sound.
- A thermometer registered
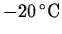 outside and then was brought into the house where the temperature was
outside and then was brought into the house where the temperature was
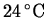 . After 5 minutes, it registered
. After 5 minutes, it registered
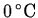 . When will it register
. When will it register
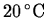 ?
?
- Suppose that for a certain drug, the following results were
obtained. Immediately after the drug was administered, the
concentration was 6.9 mg/ml. Four hours later, the concentration had
dropped to 2.4 mg/ml. Determine the value of
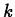 for this drug.
for this drug.


Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
William W. Farr
2003-12-09
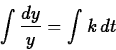
![]() , after 5730 years, half of it
will have undergone decay.
So, if the half-life is of an element Z is
, after 5730 years, half of it
will have undergone decay.
So, if the half-life is of an element Z is ![]() years, it must be
that
years, it must be
that
![]() , so that
, so that ![]() and
and
![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() as follows. The value of
as follows. The value of ![]() is the
initial concentration, so we have
is the
initial concentration, so we have