For each function below,
- (a)
- Find the Taylor Polynomial for f(x) about x=a of order n for each function given below. Use the command TayPlot to plot the graph of the function as well as the approximating polynomials on the same plot using an interval of length 4 centered about x=a. By looking at this plot, can you find an interval of x values for which Pn(x) would approximate f(x) very well?
- (b)
- Use Pn(x) for the given n in each case to approximate the function at the given x value. To determine the accuracy of this approximation, use the Taylor remainder term
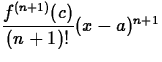 to estimate the error. In order to do this, you will want to find the least upper bound for f(n+1)(c) where c is between a and x. Compare this estimation with the actual error |f(x)-Pn(x)|. What must be true about the relationship between the estimated error and the actual error?
to estimate the error. In order to do this, you will want to find the least upper bound for f(n+1)(c) where c is between a and x. Compare this estimation with the actual error |f(x)-Pn(x)|. What must be true about the relationship between the estimated error and the actual error?
- (c)
- Experiment with different values of n in the plot of the actual error to find the smallest possible degree of the Taylor Polynomial that approximates f on the interval from a to x with an error no greater than 0.0001. Use this value of n and Pn(x) to approximate f at the given x value and show that your approximation agrees with the actual answer to within 3 decimal places.
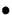
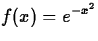 , a=0, x=0.5, n=8
, a=0, x=0.5, n=8
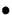
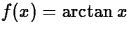 , a=1,
, a=1, 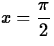 radians, n=3
radians, n=3
![]()
![]()
![]()
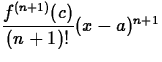 to estimate the error. In order to do this, you will want to find the least upper bound for f(n+1)(c) where c is between a and x. Compare this estimation with the actual error |f(x)-Pn(x)|. What must be true about the relationship between the estimated error and the actual error?
to estimate the error. In order to do this, you will want to find the least upper bound for f(n+1)(c) where c is between a and x. Compare this estimation with the actual error |f(x)-Pn(x)|. What must be true about the relationship between the estimated error and the actual error?
![]()
![]() , a=0, x=0.5, n=8
, a=0, x=0.5, n=8
![]()
![]() , a=1,
, a=1, ![]() radians, n=3
radians, n=3