TEST 2 MA-4451
SOLUTIONS
1.We look for a solution in the form:
![]()
where h satisfies:
![]()
or equivalently:
![]()
By integrating twice:
![]()
Imposing h to be bounded for r = 0 and using the boundary condition, we determine h to be:
![]()
The problem is thus reduced to solving a homogeneous PDE for v:
![]()
2. See notes.
3.a. The problem reduces to:
![]()
![]()
b. The boundary condition becomes:
![]()
c. The equation in R is a Bessel equation of order 0. The general solution is:
![]()
Since the solution has to be bounded at 0, we obtain that B = 0. From the boundary condition we get:
![]()
from where we determine ![]() and thus the eigenvalues
and thus the eigenvalues ![]() :
:
![]()
with ![]() solutions of
solutions of ![]() .
.
Once the eigenvalues are determined we can find T:
![]()
d. The solution is:
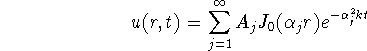
In order to satisfy the initial condition we have to determine the coefficients such that:
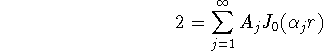
From the formula for the coefficients (see table 4):
![]()
From the properties of Bessel functions (see table 2) we can compute the above integral. Finally:
![]()