

Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
Subsections
The purpose of this lab is to acquaint you with using Maple to compute
partial derivatives.
To assist you, there is a worksheet associated with this lab that
contains examples and even solutions to some of the exercises. You can
copy that worksheet to your home directory by going to your computer's Start menu and choose run. In the run field type:
\\filer\calclab
when you hit enter, you can then choose MA1024 and then choose the worksheet
Pardiff_start_C13.mw
Remember to immediately save it in your own home directory. Once you've copied and saved the worksheet, read through the background on the internet and the background of the worksheet before starting the exercises.
A differentiable function, 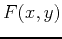 , of two variables has two partial
derivatives:
, of two variables has two partial
derivatives:
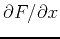 and
and
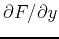 . As you have learned in class, computing partial derivatives is
very much like computing regular derivatives. The main difference is
that when you are computing
. As you have learned in class, computing partial derivatives is
very much like computing regular derivatives. The main difference is
that when you are computing
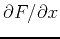 , you must treat
the variable
, you must treat
the variable 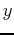 as if it was a constant and vice-versa when computing
as if it was a constant and vice-versa when computing
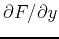 .
.
The Maple commands for computing partial derivatives are D
and diff. The Getting Started worksheet has examples
of how to use these commands to compute partial derivatives.
- Compute the two first order partial derivatives and the three distinct second order partial derivatives of
at the point
using the diff command and then again using the D command.
- Given the function
do the following:
- a)
- Plot the function and the plane
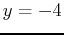 on the same graph. Use plotting ranges
on the same graph. Use plotting ranges
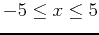 ,
,
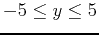 ,
,
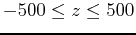 .
.
- b)
- Graph the two-dimensional intersection of the plane
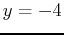 . Be sure to use
. Be sure to use 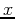 and
and 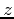 ranges that are consistent with your ranges in part a.
ranges that are consistent with your ranges in part a.
- c)
- Does your two-dimensional graph look like the intersection from your tree-dimensional graph?
- Given:
, find the equation of the plane tangent to the surface at
. Plot the surface and the tangent plane on the same graph over the intervals
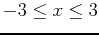 ,
,
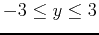 .
.
- Given:
- a)
- Find all points on the graph where the tangent plane is horizontal.
- b)
- Find the equation of each horizontal plane and plot them on the same graph as the function
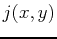 . Use plotting ranges
. Use plotting ranges
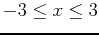 ,
,
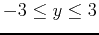 .
.


Next: About this document ...
Up: lab_template
Previous: lab_template
Dina J. Solitro-Rassias
2013-01-20
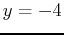 on the same graph. Use plotting ranges
on the same graph. Use plotting ranges
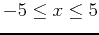 ,
,
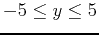 ,
,
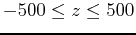 .
.
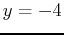 . Be sure to use
. Be sure to use 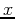 and
and 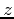 ranges that are consistent with your ranges in part a.
ranges that are consistent with your ranges in part a.
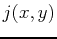 . Use plotting ranges
. Use plotting ranges
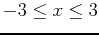 ,
,
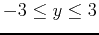 .
.