- a.
- Do you agree that a histogram is all she
needs to look at? Why or why not?
ANS: No, since a histogram cannot detect non-stationarity.
- b.
- What alternative display(s) would you
suggest she look at? In what way(s) would your
suggested display(s) help her better evaluate the
production process' performance?
ANS: A time series plot of force versus time. It can tell her when the process begins becoming non-stationary, and therefore help in quickly dientifying problems.
- a.
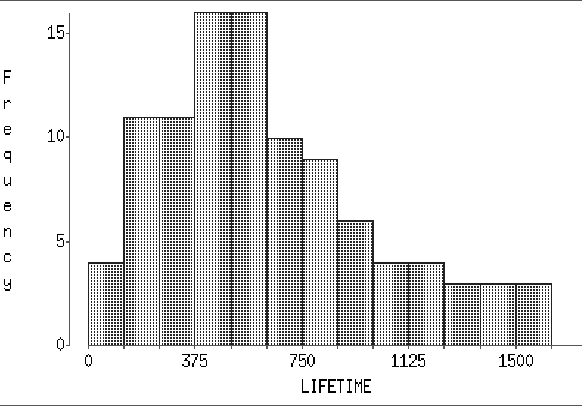
- On the graph note the approximate location
of the mean.
ANS: The mean is at 635. Anything close is ok.
- b.
- Give the value of one meaningful measure of
location and one of spread for these data. Tell what each measures.
ANS: Location: mode, 500, which is at the center of the highest bars, or the median, 565.5, above which and below which lies half the data. Spread: IQR, 837.5-358.5=479, the spread of the middle half of the data.
- c.
- Obtain the 5 number summary of the data. If
the 10 largest impeller lifetimes are 1605, 1573, 1547, 1474, 1471,
1395, 1352, 1285, 1272, and 1237, and if the smallest observation is
48, construct a box-and-whisker plot of the data. Are any outliers
suggested by this plot? If so, what are their values?
ANS: The lower adjacent value is 48, which is the smallest data value greater than
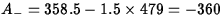 . The upper
adjacent value is 1547, which is the largest data value less than
. The upper
adjacent value is 1547, which is the largest data value less than
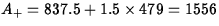 . The rest of the five number summary
consists of Q1=358.5, Q2=565.5 and Q3=837.5. The boxplot is
in Figure 2.
. The rest of the five number summary
consists of Q1=358.5, Q2=565.5 and Q3=837.5. The boxplot is
in Figure 2.
- d.
- A new water pump of the same type has just
been put into service. If you had to supply one number
as an estimate of the lifetime of its impeller blade,
what number would you use? Tell how you obtained this
number and why you chose it.
ANS: The mode, 500, which is at the center of the highest bars. These are the bars containing the greatest number of observations.
- a.
- Was this study a controlled experiment? Why
or why not?
ANS: No. Treatments were not assigned to experimental units.
- b.
- Identify the response variable.
ANS: Outcome: death or not within 30 days.
- c.
- Explain why this study does not establish
conclusively that right heart catheterization is causing a
greater number of deaths in critically ill heart patients than
would otherwise occur.
ANS: Because researchers were not allowed to control assignment of treatment to patients, or to control or randomize with respect to nuisance variables, the results can only suggest an association, not establish cause-effect.
- d.
- You are a consultant called in to design a
follow-up study to establish conclusively if right heart
catheterization is causing a greater number of deaths in
critically ill heart patients than would otherwise occur. What
kind of study would you design? Describe how and why you would
use blocking, randomization and replication.
ANS: I would design a controlled experiment in which treatments (right heart catheterization or alternative procedures) were assigned to patients by the researchers. Blocking could involve factors such as hospital, surgeon, severity of patient illness, patient age, patient gender, etc., and would be used to reduce variation in the responses due to those factors. Randomization would be used for whatever was not blocked to remove unsuspected sources of bias. For example, within blocks, treatments would be assigned to patients at random.
![\begin{figure}
\centerline{\includegraphics*[height=2.0in,width=6in]{test1f2.ps}}
\vspace{2ex}\end{figure}](img4.gif)