
Now we can use the integral test to show that our series converges. We will also be able to use our estimate of the error term to decide how many terms in the sum are needed to approximate S to a given accuracy.
To see if the series converges, we just have to compute the integral

which can be done in Maple with the command shown below.
> int(f(x),x=1..infinity);

The integral converges, so the sum converges.
Now, suppose we wanted to compute the sum to an accuracy of
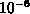 . We can use our error estimate to find a value of n that
will give us the desired accuracy. That is, we need to find a value of
n such that
. We can use our error estimate to find a value of n that
will give us the desired accuracy. That is, we need to find a value of
n such that

The following Maple commands show how to do this.
> error := n -> int(f(x),x=n..infinity);
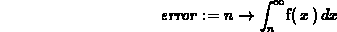
> evalf(error(10));

> evalf(error(11));

> evalf(solve(error(n)=10^(-6),n));

The final result means that we would have to take at least 21 terms
in the sum to approximate S to within an error of 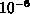 .
.