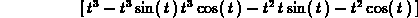> with(linalg):
Warning: new definition for norm Warning: new definition for trace
> with(CalcP):
> u := vector([1,2,3]);

> f := t-> vector([t,t^2,t^3]);
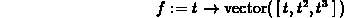
> g := t -> vector([cos(t),sin(t),t]);
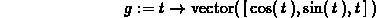
> h := t -> vector([cos(t),sin(2*t)]);
To add vectors, or multiply them by scalars, you can use the Maple add and scalarmul commands, or use standard math notation and use the evalm command.
> add(u,g(t));
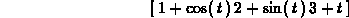
> evalm(t^4*u+2*f(t)-g(t));
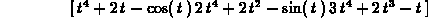
> scalarmul(u,t^2);

The individual components of a vector are also available in Maple, as shown below. You can use this to extract the individual functions for plotting or further manipulation.
> u[3];

> f(t)[1];

> g(t)[2];

The linalg package has procedures for the dot product and the cross product. The latter procedure, however, works only on vectors with three components and the former procedure requires two vectors with the same number of components, so beware. Some examples are shown below.
> dotprod(u,f(t));

> crossprod(u,g(t));
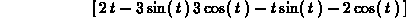
> crossprod(f(t),g(t));